A Step-by-Step Guide to Gen AI Workflows

Watch the full video here
Quick background about me:
I recently tackled a common challenge in our organization – creating comprehensive surveys that actually generate actionable insights. What traditionally took days of expert work can now be accomplished in 20-30 minutes with a well-designed Gen AI workflow, I’d say.
In this post, I’ll walk you through how to build effective AI workflows step by step, using my survey creation workflow as a practical example. Whether you’re new to AI workflows or looking to improve your approach – these principles will help you design processes that deliver consistent, high-quality results.

Watch the full video here
Why Build AI Workflows?
Before diving into the „how,“ let’s talk about the „why.“ This is actually easier than you might think. A well-designed AI workflow can actually save significant time on repetitive tasks, ensures consistency across outputs, and above all makes expertise more accessible to your entire team.
What this means is, it breaks complex tasks into manageable steps and creates reusable processes that improve over time. In my survey example, we transformed what was once a specialized skill – requiring deep knowledge of survey design principles – into a streamlined process anyone on the team can follow.
Step 1:
Interview an Expert
The first step in creating any effective workflow is understanding what experts currently do to accomplish the task. This has to do with the fact that you need to capture their thought process, not just their output.
Here’s a list of excellent questions to ask an expert – I personally use these relatively frequently:
What exactly is the goal of the workflow?
What does the result/target artifact(s) need to include?
What information did you need in order to start the task?
What was your thought process from beginning to end?
How did you evaluate the quality of your sources, data and intermediary steps?
Also, let me say upfront: Even a quick 15-30 minute conversation with a knowledgeable colleague can save you hours of frustration later and help align your workflow with what’s actually needed.
For my survey workflow, I spoke with our research team to understand their process for designing surveys that yield meaningful insights. This conversation revealed crucial requirements: surveys need to be engaging but brief, questions must connect to clear hypotheses, and above all – analysis needs to be planned before deployment.
Step 2:
Define the Goal
Every effective workflow needs a concrete goal focused on creating a specific artifact that solves a problem. This means you can’t just say „help teams understand their customers better“ – that’s too abstract.
For the survey workflow, I defined two clear artifacts as goals:
A finished survey with all sections, questions, and explanatory text
An analysis and interpretation guide to help make sense of the collected data
Notice how these are tangible outputs rather than abstract goals. This is particularly important because it makes it easier to evaluate success and iterate on your workflow.
Step 3:
Craft Your Workflow
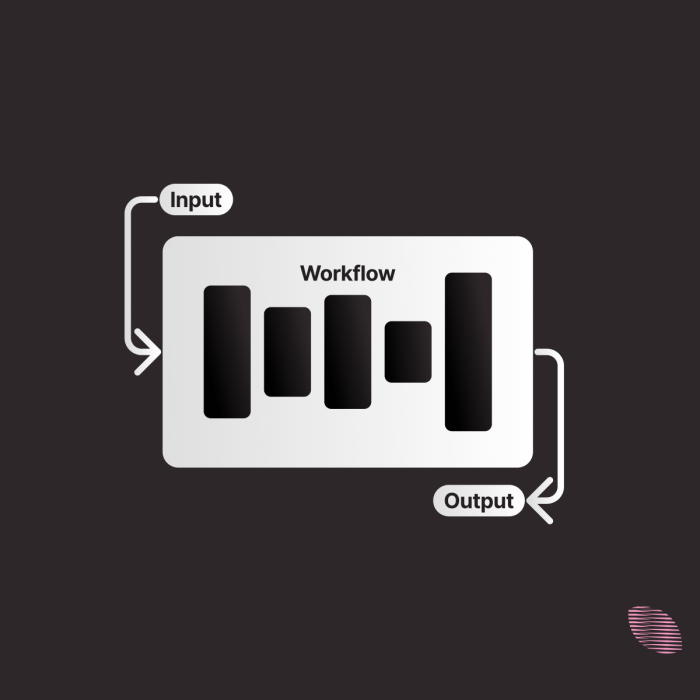
With your goal defined, break down the process into logical steps. Think about what information is needed at each stage (inputs), what is produced at each stage (outputs), and what tools will be used.
For my survey workflow, I identified these key steps:
Define the research question
Expand the main question into sub-questions
Draft hypotheses for each sub-question
Select the most relevant hypotheses to test
Draft survey questions based on selected hypotheses
Generate the complete survey with all sections
Critique the survey and improve it
Create an analysis and interpretation guide
Each step has clear inputs and outputs. What this means is, the „Expand Research Question“ step takes the main research question and research context as inputs and produces expanded sub-questions as output.
Step 4:
Design Your Prompts
This is where the magic happens, I’d say. Well-crafted prompts are above all the building blocks of effective AI workflows.
An effective prompt should follow this structure:
Introduction: Tell the AI its role and main task
Context Section: Provide necessary background information
Detailing Section: Reinforce and detail the task after providing context
Closing: Include language constraints and final guidance
Let’s examine the prompt from the „Expand Research Question“ step:
You are a Research Assistant and need to expand the Main Research Question into Sub-Questions that help explore smaller nuances of the initial question.
Context of Research:
„““{{Research Context}}“““
Main Research Question:
„““{{Research Question}}“““
Make a List starting with the Main Research Question and generated Sub-Questions. Ensure to mark each clearly.
Make it {{Language}}. Let’s Think Step by Step:
This prompt defines the AI’s role as a Research Assistant, provides context through variables that can be easily replaced, gives clear instructions on the expected output format, and ends with language specification and the „Let’s think step by step“ technique to improve quality.
I personally recommend: Always use the largest models available first – for LLMs this means Reasoning Models like Claude 3.5 Sonnet or GPT-4. These models „think“ before answering and are able to produce more complex and more reliable output in one single step than other types of LLMs.
Let’s examine the prompt from the „Expand Research Question“ step:
You are a Research Assistant and need to expand the Main Research Question into Sub-Questions that help explore smaller nuances of the initial question.
Context of Research:
„““{{Research Context}}“““
Main Research Question:
„““{{Research Question}}“““
Make a List starting with the Main Research Question and generated Sub-Questions. Ensure to mark each clearly.
Make it {{Language}}. Let’s Think Step by Step:
This prompt defines the AI’s role as a Research Assistant, provides context through variables that can be easily replaced, gives clear instructions on the expected output format, and ends with language specification and the „Let’s think step by step“ technique to improve quality.
Step 5:
Choose a Test Case
Before implementing your entire workflow, select a realistic test case. This is actually more important than you might think.
For my survey workflow, I chose to create an employee happiness survey for our digital agency, which has a high proportion of senior roles and few junior positions. I also made a little documentation of all available questions and fields in Microsoft Forms to use this documentation as input for the survey drafting step.
This specific context gave me the constraints needed to properly test the workflow.
Step 6:
Start Testing
When testing your workflow, follow these principles:
Test early and focus on one prompt at a time
Iterate on each prompt until you’re satisfied before moving to the next
Identify and fix issues immediately rather than testing the entire workflow at once
This has particularly to do with the fact that nothing is more frustrating than a workflow that doesn’t work and you have no idea why it doesn’t work.
In my testing, I discovered that the prompt for drafting hypotheses needed refinement to generate better connections to the research questions. By fixing this single prompt before moving on, I avoided compounding errors further down the workflow.
Step 7:
Document Steps with Clear Input-Output Relationships
For each step in your workflow, clearly document:
Description: A brief explanation of what the step accomplishes
Team or Person responsible: Who executes this step
Time: Estimated duration to complete
Inputs: What information is needed
Outputs: What this step produces
Blockers & Bottlenecks: Potential challenges
Tools: AI models or platforms used
Prompt: The exact prompt text with variables clearly marked
Cost: Resource requirements (time, subscription fees, etc.)
This documentation makes your workflow transparent, shareable, and improvable. What this means is, team members can understand how the pieces fit together and can actually contribute to improving the process.
Step 8:
Refine Based on Results
Once you’ve tested individual prompts, run through the complete workflow and evaluate the final output against your goal.
For my survey workflow, I compared the generated survey with professional surveys our research team had created previously. I looked for question clarity, logical flow between sections, and above all whether the analysis guide would produce actionable insights.
Step 9:
Organize for Future Use
Once your workflow delivers satisfactory results, organize it for easy access and future use:
Keep your documentation clean and updated
Mark which steps have been tested successfully
Consider taking breaks between workflow development sessions
Resist the urge to automate too early – ensure the workflow is stable first
Let me say upfront: If you keep your board organized and clean, you will be able to keep going way faster when you come back to it.
Common Challenges
and Solutions
❌ Challenge: Prompts aren’t producing consistent results
✅ Solution: Add more structure to your prompts and be specific about the format you want. Use variables for customization while keeping the core instruction consistent.
❌ Challenge: Workflow steps don’t connect smoothly
✅ Solution: Ensure outputs from one step match the expected inputs for the next. What this means is, sometimes you’ll need to add intermediate steps or refine prompts.
❌ Challenge: The final output doesn’t meet quality standards
✅ Solution: Work backward to identify which step is introducing issues. Sometimes adding a critique step can help improve quality.
Real-World Impact
The Survey Workflow in Action
Let’s see how this all works in practice with our survey workflow example:
We begin with a clear research question: „How happy are people working at the company?“
This expands into sub-questions covering areas like work environment, project allocation, leadership, career development, and more. Hypotheses are drafted for each area, such as „Senior employees feel their specialized skills are underutilized.“
The most relevant hypotheses are selected based on the research goals, survey questions are drafted to test these hypotheses, and a complete survey is generated with proper sections, including demographics, overall happiness assessment, workload questions, leadership evaluations, etc.
The result: A comprehensive employee happiness survey that would typically take days to create but now takes under 30 minutes.
Ready to build your own AI workflow?
Start small:
Choose a repetitive task you know well
Talk to others who perform this task regularly
Define a clear artifact as your goal
Map out the logical steps
Create prompts for each step, testing each step with a specific example
Refine until satisfied
Document for future use
Remember that workflow design is a skill that improves with practice. Some people are really good at workflow design, but with any task – some people like it and some don’t. It is perfectly fine if you struggle with workflow design. You don’t have to construct workflows – this skill is not inherently more valuable than any other skill
Conclusion
Building effective Gen AI workflows isn’t about complex technical skills – it’s about clearly defining goals, breaking down processes into logical steps, and writing prompts that guide AI to produce what you need.
What this means is, by following the steps outlined in this post, you can transform time-intensive tasks – like creating comprehensive surveys – into efficient, repeatable processes. Your workflows might start simple, but they’ll grow in sophistication as you learn what works.
Remember to:
Start with expert input
Define concrete goals
Break processes into discrete steps
Test early and often
Document thoroughly & organize for reuse
Above all:
Resist the urge to automate too quickly. Try to resist automating the workflow as much as possible – naturally it’s going to change over time and with automation there comes a whole layer of complexity that just makes it harder.
What task will you transform with your first Gen AI workflow? If you have ideas, problems, fears, thoughts, or use cases you want to solve concerning the use of GenAI tools, please feel free to reach out.